Uncovering System Weaknesses: A Practical Approach to Vulnerability Scanning#
Uncovering System Weaknesses: A Practical Approach to Vulnerability Scanning#

\
INTRODUCTION
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, identifying and mitigating vulnerabilities is a critical step in ensuring the security and integrity of systems. This report documents the results of a vulnerability scan performed on a specified host, with the goal of uncovering potential weaknesses that could be exploited by attackers.
The scan was conducted using the Nmap tool, leveraging the Nmap Scripting Engine (NSE) to identify outdated software, open ports, and potential misconfigurations. These vulnerabilities, if left unaddressed, could lead to unauthorized access, data breaches, or service disruptions. This report outlines the vulnerabilities found, provides an assessment of the associated risks, and offers recommended mitigation steps to enhance the security posture of the target system.
The findings will help system administrators and security professionals prioritize remediation efforts to reduce the attack surface and safeguard critical assets.
Scope of the Vulnerability Assessment
This vulnerability assessment focuses on the network within the private IP address range 192.168.37.0/24, which represents a local subnet in a private network environment. The primary objective is to identify and document security weaknesses, including open ports, outdated software, and misconfigurations, that could potentially be exploited by attackers.
The scope of this assessment includes all devices connected within the 192.168.37.0/24 range. This network segment typically includes routers, servers, workstations, IoT devices, or other infrastructure components that are critical to the network’s operation. The assessment will involve the use of network scanning tools, specifically Nmap, to:
- Discover live hosts within the subnet.
- Scan for open ports and services.
- Identify vulnerabilities in services or operating systems.
- Analyze potential misconfigurations or security gaps.
The results of this assessment will provide a clear understanding of the network’s security posture and inform recommendations for improving security through patch management, configuration adjustments, and the closure of unnecessary ports or services.
TOOLS USED:
1.Vimware machine
2.Nmap
Step 1: Host Discovery (Check if Hosts are Up)
The first step before diving into vulnerability scanning is to identify which hosts are up and responsive within the network range 192.168.37.0/24. This helps ensure you’re only scanning active devices and not wasting resources on inactive ones.
Before performing the vulnerability scan, we will use a simple ping scan with Nmap to check which hosts in the subnet are alive.
nmap -sn 192.168.37.0/24
expected output:

\
I have identified that there are 5 live hosts, I can now proceed with a more detailed port or vulnerability scan on these specific IPs.
Step 2: Port Scanning on Discovered Hosts
Once you have identified which hosts are up and responding in Step 1, the next logical step is to perform a port scan on those live hosts. This will help you discover:
- Which services (e.g., web servers, SSH, databases) are running.
- The port numbers they are using.
- Whether these ports are publicly accessible or filtered.
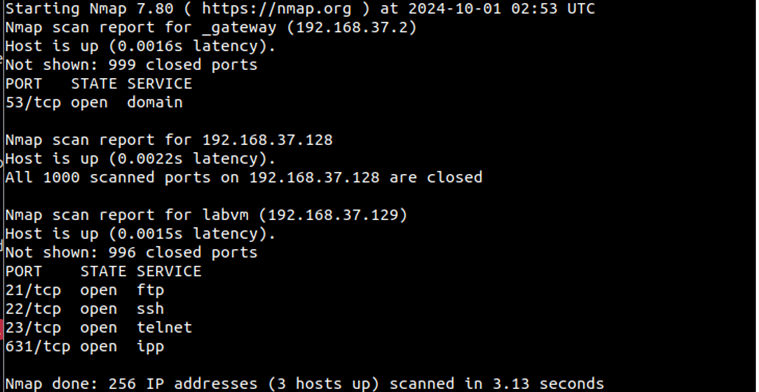
nmap 192.168.37.0/24
\
As we can see from the scan results, there are 4 ports open, and there are different services running on each port. The scan we just performed, however, is a very basic scan and will only scan the top 1000 ports for basic information. In the next step, we will run a more advanced scan.
Goal: Discover all open ports and services running on the live hosts identified in Step 1.
Action: Perform a detailed port scan on each host to see which services are exposed.
Outcome: Identify potentially vulnerable services running on those ports, which can be analyzed further for mitigation.
Step 3. service enumeration
in this step, we will be scanning the same target, but with a more advanced scan. Let’s say we want to determine the versions for the services running on each port, so that we can determine if they are out of date and potentially vulnerable to exploitation. We also want to determine the operating system of the webserver running the target site. We will run the following scan to determine this information:
sudo nmap -v -sT -sV -O 192.168.37.0/24
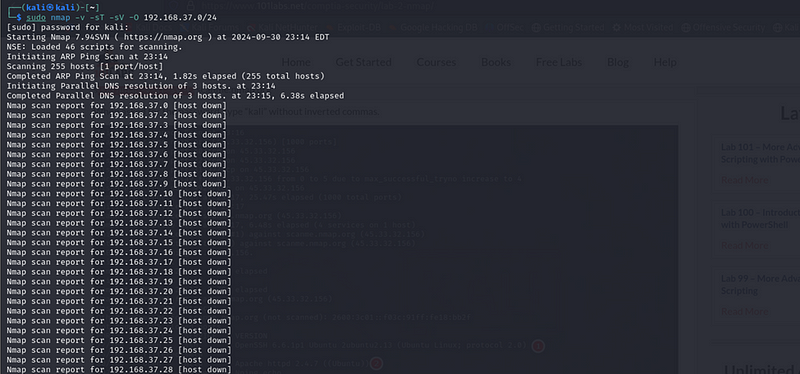
The process is a bit long I had to capture just relevant aspects
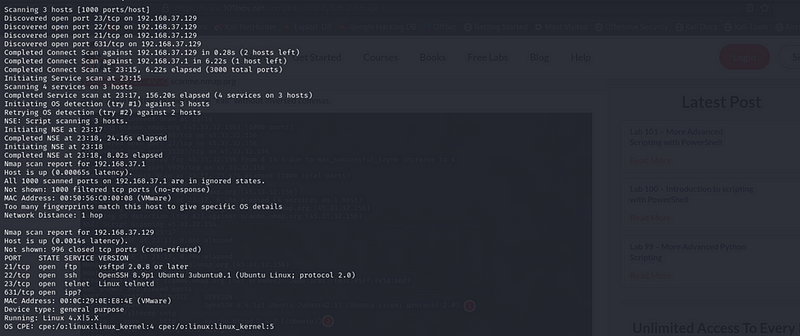
The Nmap scan reveals that the host at IP address 192.168.37.129 is active and responsive, with a low latency of 0.0014 seconds. The scan indicates that 996 TCP ports are closed, with no connection established. This report focuses on the open ports and their associated services, as well as potential security implications.
Open Ports and Services
- Port 21: FTP (vsftpd 2.0.8 or later)
- Status: Open
- Details: The FTP service is running vsftpd version 2.0.8 or later, which may have known vulnerabilities.
- Security Considerations:
- Anonymous Login: Check if anonymous login is enabled, as this can lead to unauthorized access.
- Configuration Issues: Ensure proper permissions are set on FTP directories to prevent unauthorized file access.
- Port 22: SSH (OpenSSH 8.9p1)
- Status: Open
- Details: OpenSSH version 8.9p1 is running on the server.
- Security Considerations:
- Brute Force Protection: Ensure that strong passwords are enforced and consider implementing measures to mitigate brute force attacks, such as fail2ban.
- Vulnerabilities: Research known vulnerabilities associated with this version of OpenSSH.
- Port 23: Telnet (Linux telnetd)
- Status: Open
- Details: The system is running a Telnet service, which is considered insecure due to unencrypted communication.
- Security Considerations:
- Plaintext Credentials: All data, including passwords, are transmitted in plaintext, making it vulnerable to interception.
- Recommendation: Disable Telnet and switch to SSH for secure remote access.
System Information
- MAC Address: 00:0C:29:0E:E8:4E (indicates the device is running on VMware).
- Device Type: General Purpose
- Operating System: Likely running a version of Linux (4.X or 5.X), with specific details indicating a kernel version between 4.15 and 5.8.
- Uptime: Approximately 38 days since the last reboot, which may indicate a stable service if security updates have been applied.
- Network Distance: 1 hop, indicating direct connectivity.
Recommendations
- Update Services: Ensure that all running services, particularly vsftpd and OpenSSH, are updated to their latest versions to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Secure Configuration: Disable Telnet and enforce the use of SSH for all remote access. Ensure FTP is configured securely.
- Regular Scans: Conduct regular vulnerability assessments and penetration tests to identify and remediate potential weaknesses.
- Monitor Logs: Regularly review system logs for unusual access patterns or failed login attempts, particularly for SSH.
I had to do the last essential scan which would be imperative to my reconnaissance:
Sudo nmap -sv –script
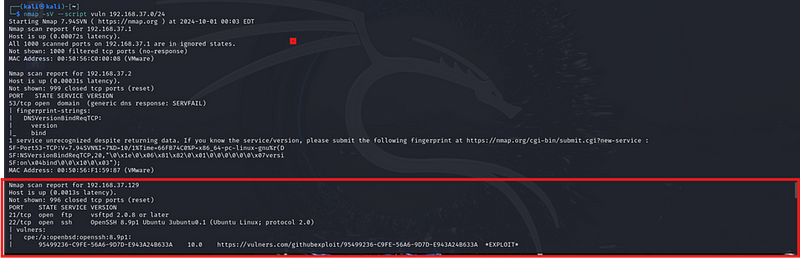
\
Host Findings
- 192.168.37.1
- Status: Up
- Ports: All 1000 scanned ports are filtered (no response).
- MAC Address: 00:50:56:C0:00:08 (VMware)
- 192.168.37.2
- Status: Up
- Ports:
- 53/tcp: Open (DNS)
- Version: Generic DNS response: SERVFAIL
- MAC Address: 00:50:56:F1:59:87 (VMware)
- 192.168.37.129
- Status: Up
- Ports:
- 21/tcp: Open (FTP) — vsftpd 2.0.8 or later
- 22/tcp: Open (SSH) — OpenSSH 8.9p1 Ubuntu 3ubuntu0.1
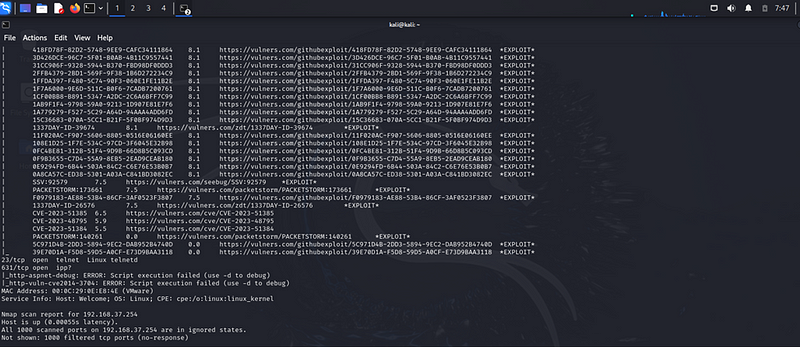
- Vulnerabilities:
§ Several high-risk CVEs and exploits related to OpenSSH:
§ CVE-2023–38408 (Severity: 9.8)
§ CVE-2023–28531 (Severity: 9.8)
§ Multiple exploits listed on various platforms.
Recommendations
- For 192.168.37.1: all ports are filtered. It could indicate a firewall configuration that is blocking Nmap.
- For 192.168.37.2: Monitor DNS responses, particularly the SERVFAIL response, to determine any misconfigurations.
- For 192.168.37.129:
- Immediate action is required to patch the SSH service due to multiple high-severity vulnerabilities.
- Review FTP service security settings, considering upgrading or configuring for better security.
Conclusion
The scan indicates that while the host is operational with several open services, there are significant security implications, especially regarding the use of Telnet and the potential for vulnerabilities in FTP. Proper hardening and regular monitoring are crucial to maintaining the security of this system.
\
Exported from Medium on February 13, 2025.